User’s Hardware Manual_V1.2
Document classification: □ Top secret □ Secret □ Internal information ■ Open
Copyright
The copyright of this manual belongs to Baoding Folinx Embedded Technology Co., Ltd. Without the written permission of our company, no organizations or individuals have the right to copy, distribute, or reproduce any part of this manual in any form, and violators will be held legally responsible.
Forlinx adheres to copyrights of all graphics and texts used in all publications in original or license-free forms.
The drivers and utilities used for the components are subject to the copyrights of the respective manufacturers. The license conditions of the respective manufacturer are to be adhered to. Related license expenses for the operating system and applications should be calculated/declared separately by the related party or its representatives.
Revision History
Date |
Manual Version |
SoM Version |
Carrier Board Version |
Revision History |
|---|---|---|---|---|
06/06/2024 |
V1.0 |
V1.0 |
V1.0 and Above |
Initial Version |
19/09/2024 |
V1.1 |
V1.0 |
V1.0 and Above |
Adding note: only RK3562 has CAN interface, and only RK3562. |
21/11/2025 |
V1.2 |
V1.0 |
V1.0 and Above |
Adding 2.6.2 SoM Anti Vibration Design Guidelines. |
Overview
This manual is designed to help users quickly familiarize themselves with the product, understand interface functions and configuration, and primarily discusses the interface functions of the development board, interface introductions, product power consumption, and troubleshooting issues that may arise during use. Some commands were commented to make it easier for you to understand (adequate and practical for the purpose). For information on pin function multiplexing, hardware troubleshooting methods, etc., please refer to Forlinx’s “OK3562J-C Pin Multiplexing Comparison Table” and “OK3562J-C Design Guide.”
There are total four chapters:
Chapter 1. is CPU overview, briefly introducing its performance and applications;
Chapter 2. is comprehensive introduction to the SoM, including connector pins explanations and function introductions;
Chapter 3. is comprehensive introduction to the development board, divided into multiple chapters, including both hardware principles and simple design ideas;
Chapter 4. mainly describes the board’s power consumption performance and other considerations.
A description of some of the symbols and formats associated with this manual:
Format |
Meaning |
|---|---|
Note |
Note or information that requires special attention, be sure to read carefully. |
📚 |
Relevant notes on the test chapters |
🛤️ |
Indicates the related path. |
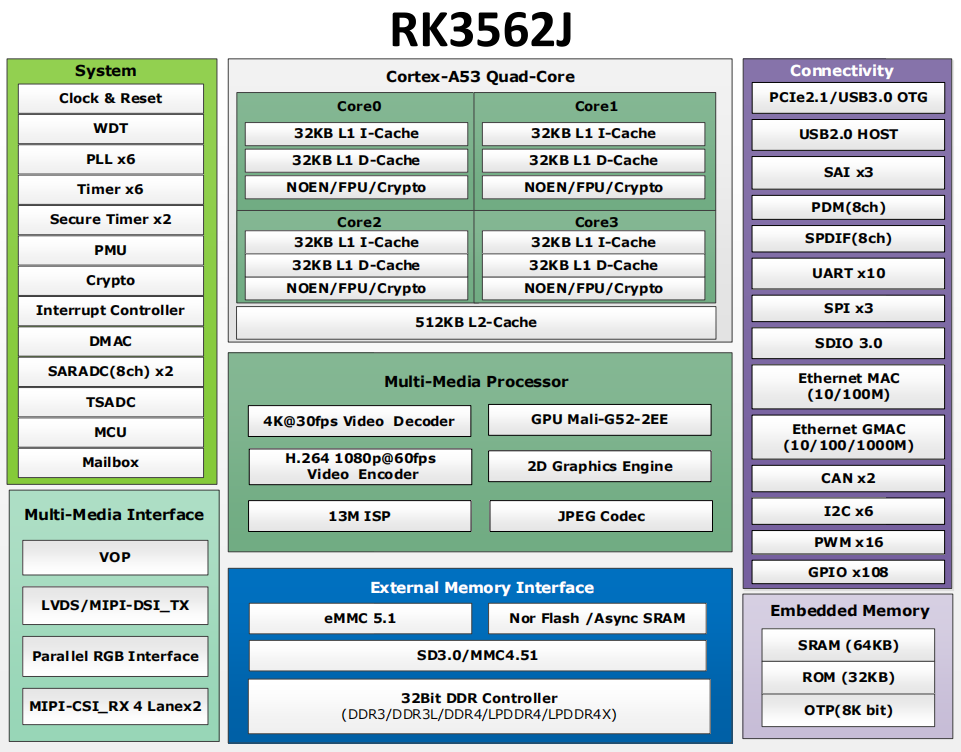
1. Rockchip RK3562J Description
The RK3562J is a high - performance, low - power quad - core application processor specifically designed for electronic devices.
The RK3562J is equipped with multiple embedded hardware engines, which can optimize the performance of high - end applications. It supports almost all - format H.264 decoding at 1080p@60fps, H.265 decoding at 4K@30fps, and H.264 encoding at 1080p@60fps. In addition, it also includes a high - quality JPEG encoder and decoder.
The RK3562J incorporates an embedded 3D GPU, ensuring full compatibility with OpenGL ES 1.1/2.0/3.2, OpenCL 2.0, and Vulkan 1.1. Moreover, it includes a special 2D hardware engine to maximize display performance and ensure smooth operation.
It features a high - performance memory interface (LPDDR4/LPDDR4X), capable of maintaining demanding memory bandwidth.
Only the RK3562J has a CAN interface.
Only the RK3562 has an NPU.
RK3562J Processor Block Diagram
2. FET3562J-C SoM Description
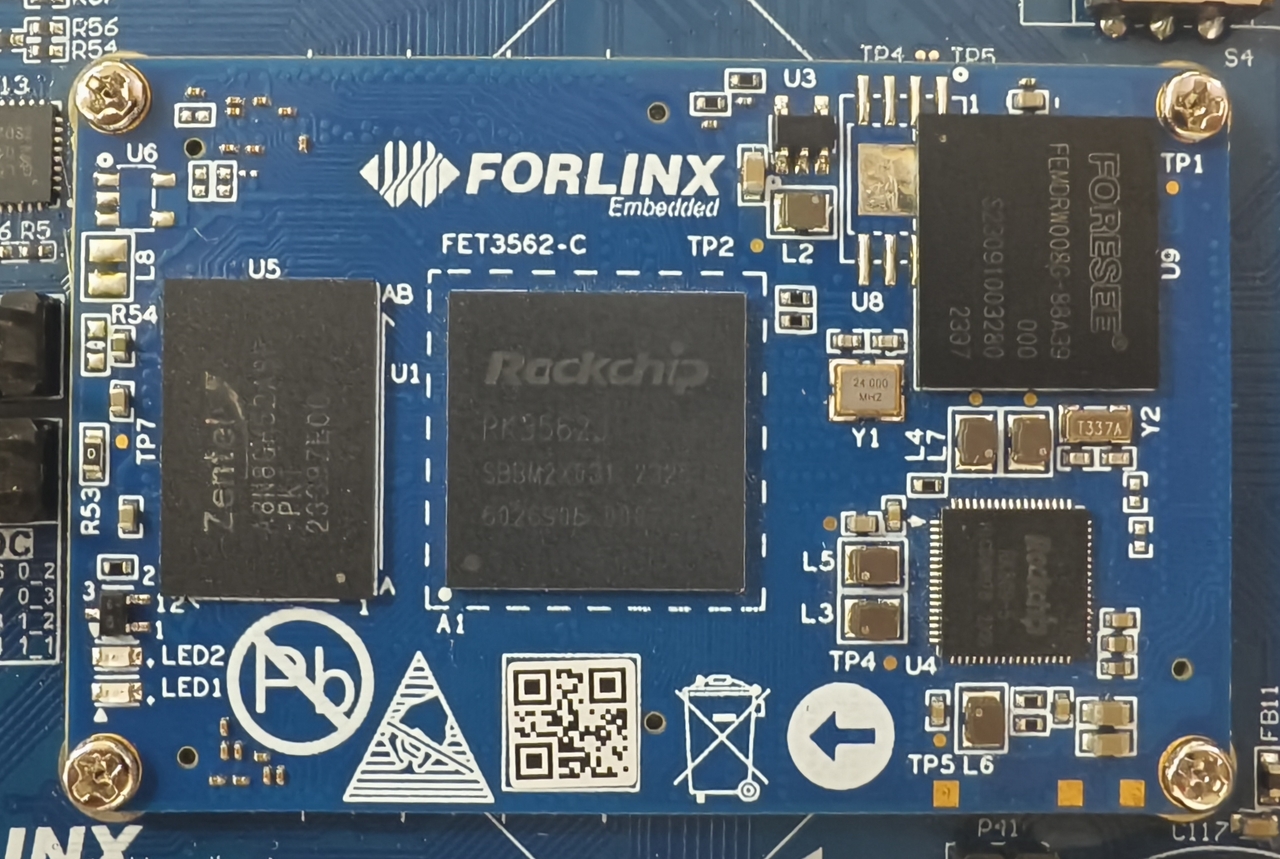
2.1 FET3562J-C SoM Appearance

Front

Back
2.2 FET3562J-C SoM Dimension Diagram

Structure size: 36mm × 56mm, dimensional tolerance ± 0.13mm, refer to DXF file for more dimensional information.
Plate making process: 1.6mm thickness, 10-layer immersion gold PCB.
SoM connector: Board to board connection, 0.5mm pitch, 80 P, male socket, height with locating post.
Carrier board connector: Board-to-board, 0.5mm pitch, 80 P, female socket, height with locating post.
Refer to Appendix for the connector dimension diagram.
It is recommended to select M2 * 2mm patch nuts for fixing the SoM and the carrier board, and the matching screw specification is M2 * 4mm.
2.3 Performance Parameters
2.3.1 System Main Frequency
Name |
Specification |
Description |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Minimum |
Typical |
Maximum |
Unit |
||
Main Frequency |
— |
1.2 |
1.8 |
GHz |
— |
RTC clock |
— |
32.768 |
— |
KHz |
— |
2.3.2 Power Parameter
Parameter |
Pin Number |
Specification |
Description |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Minimum |
Typical |
Maximum |
Unit |
|||
Main Power Supply Voltage |
VSYS |
4.75 |
5 |
5.25 |
V |
— |
No-load current |
— |
100 |
mA |
See Appendix Power Consumption Table |
||
High-load current |
— |
440 |
mA |
See Appendix Power Consumption Table |
2.3.3 Operating Environment
Parameter |
Specification |
Description |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Minimum |
Typical |
Maximum |
Unit |
|||
Operating temperature |
Operating Environment |
0 |
25 |
+70 |
℃ |
Commercial level |
Storage Environment |
-40 |
25 |
+125 |
℃ |
||
Operating Environment |
-40 |
25 |
+85 |
℃ |
Industrial-grade |
|
Storage Environment |
-40 |
25 |
+125 |
℃ |
||
Humidity |
Operating Environment |
10 |
— |
90 |
%RH |
No condensation |
Storage Environment |
5 |
— |
95 |
%RH |
2.4 SoM Interface Speed
Function |
Quantity |
Parameter |
|---|---|---|
USB2.0 |
1 |
Supports 1 x USB2.0 HOST, up to 480Mbps. |
UART(1) |
≤10 |
Supports flow control, with a maximum baud rate of 4Mbps. |
SPI |
≤3 |
Supports master and slave modes |
I2C(2) |
≤5 |
Supports standard mode 100kbit/s and fast mode 400kbit/s |
Ethernet |
≤2 |
Supports one RGMII and one RMII |
PCIe |
≤1 |
PCIe 2.1, can only be used in RC mode, only supports single lane, 5Gbps, |
USB3.0 |
≤1 |
Supports the master-slave mode of USB3.0, |
ADC(3) |
≤16 |
10bits resolution, maximum sampling rate 1MS/s |
LVDS(4) |
≤1 |
Supports VESA/JEIDA LVDS data format with resolution up to 800 X 1280 @ 60Hz |
MIPI-DSI(4) |
≤1 |
Supports 1x MIPI DSI TX, 4-lanes, resolution up to 2048 X 1080 @ 60Hz |
RGB |
≤1 |
Supports RGB 888 format with resolution up to 2048 X 1080 @ 60Hz |
MIPI-CSI |
4 |
The MIPI _ CSI _ RX0 and the MIPI _ CSI _ RX1 have two ports in total; |
SD card |
1 |
Compatible with SDIO 3.0 protocol, 4bits data bit width |
SDIO |
≤1 |
Compatible with SDIO 3.0 protocol, 4bits data bit width |
SAI(5) |
≤2 |
Supports protocol I2S, PCM, TDM, sampling rate up to 192kHz |
Audio |
The SoM has a built - in codec, which directly outputs audio analog signals. The sampling rate ranges from 48KHz to 192KHz; |
|
PDM |
≤1 |
Up to 8 channels, sampling rate up to 192KHz, master receive mode |
SPDIF |
≤1 |
|
CAN(6) |
≤2 |
Supports CAN2.0 B, data rate 1Mbps |
PWM |
≤16 |
|
GPIO |
≤79 |
Note:
The parameters in the table are the theoretical values of hardware design or CPU;
“TBD” refers to functions not yet developed;
UART0 is a debugging serial port and is not recommended to be used for other functions. Users can use up to 9 x serial ports;
I2C0 is occupied on the SoM, and the carrier board is not available;
SARADC0_BOOT and SARADC0_IN1 are related to system startup. It is not recommended to use them as general ADC. The maximum number of ADC available to users is 14;
LVDS and MIPI - DSI have pin multiplexing. You can only choose one of them for use;
I2S0 is occupied by the SoM and cannot be used on the carrier board;
Only the RK3562J has a CAN interface.
2.5 FET3562J-C SoM Pins Definition
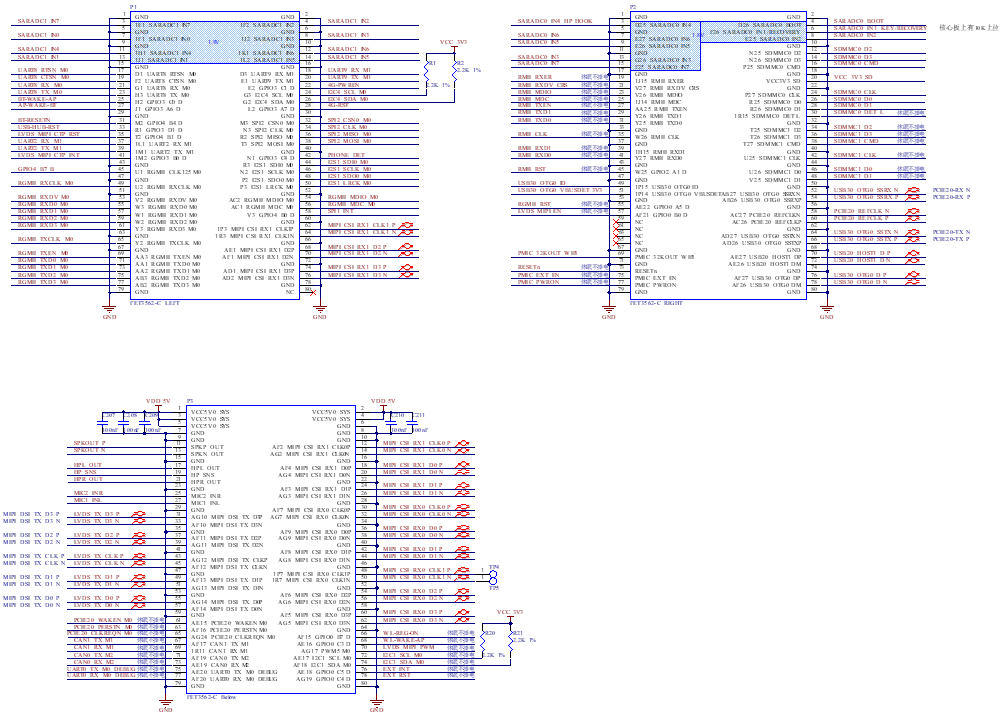
2.5.1 FET3562J-C SoM Pins Schematic
(SoM connector schematic)
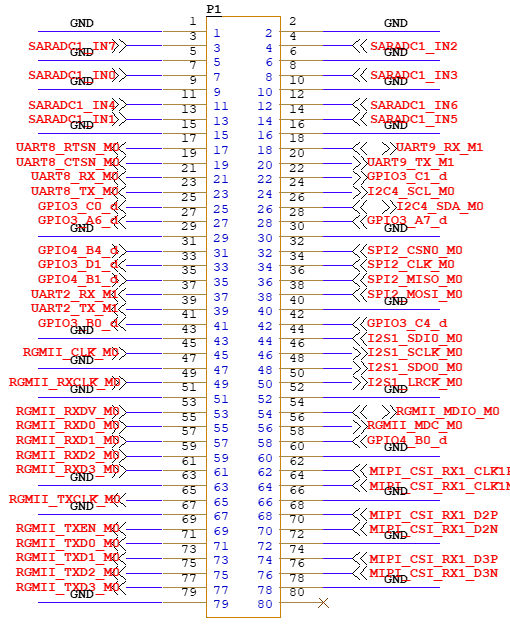

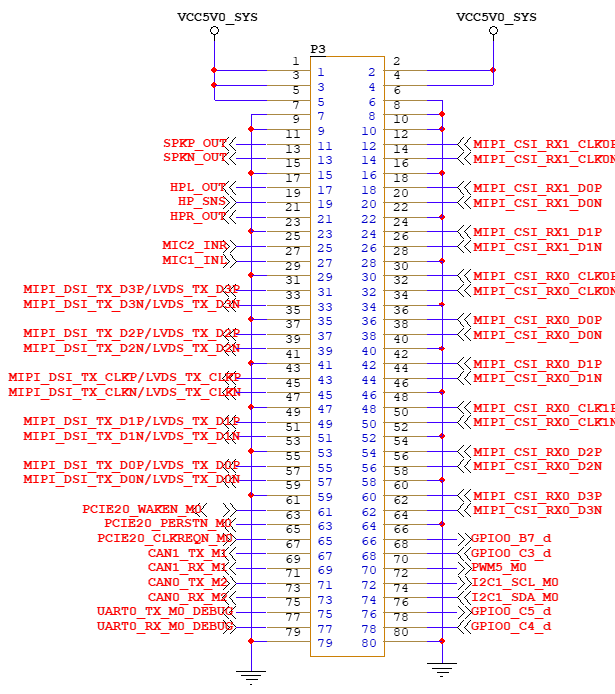
2.5.2 FET3562J-C SoM Pins Description
When you have multiple functional expansion requirements, please refer to the user guide “FET3562-C Pin Multiplexing Table”. However, for more detailed information, it is recommended to consult relevant documents, the chip datasheet, and the reference manual.
2.6 SoM Hardware Design Description
2.6.1 SoM Circuit Design Guidelines
Power Pin
Function |
Signal Name |
I/O |
Default Function |
Pin Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Power |
VCC5V0_SYS |
Power Input |
The power supply pin for the SoM is 5V, and |
|
VCC3V3_SD |
Power output |
Only used for power supply of backplane SD card, |
P2_20 |
|
GND |
Ground |
SoM power ground and signal ground, |
Function Control Pin
Function |
Signal Name |
I/O |
Default Function |
Pin Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
CPU Reset |
RESETn |
I |
SoM power reset, active low, users should not add additional |
P2_73 |
Power Enable |
PMIC_EXT_EN |
O |
Enable signal to control the |
P2_75 |
Power On/Off |
PMIC_PWRON |
I |
Low level is valid, long press to |
P2_77 |
BOOT Mode Selection |
SARADC0_BOOT |
I |
When the signal is grounded, |
P2_4 |
Reset Mode |
SARADC0_IN1_KET/RECOVERY |
I |
When the signal is grounded, |
P2_6 |
Debug Port |
UART0_TX_M0_DEBUG |
I/O |
Debugging serial port. It is recommended that the |
P3_75 |
It includes the minimum system block diagram.
FET3562J-C SoM integrates the power supply, reset monitoring circuit, and storage circuit into a compact module. The required external circuits are very simple. To form a minimal system, only a 5V power supply, as shown in the following figure:
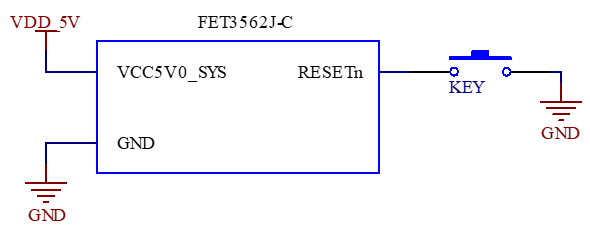
Please refer to “Appendix IV. for the minimal system schematic diagram However, in most cases, it is recommended to connect some external devices in addition to the minimal system, such as a debugging serial port, image flashing port, otherwise, users can not check whether the system is booted. After completing these steps, additional user-specific functions can be added based on the default interface definitions provided by Forlinx for the SoM.
Please refer to section 3.5 in “Chapter 3. OK3562J-C Carrier Board Description” for the peripheral circuits.
2.6.2 SoM Anti Vibration Design Guidelines
It uses M2 - sized thread - locking screws to fix the pre - set mounting holes at the four corners of the SoM. The tightening torque is controlled at 0.15 N·m. The specific assembly schematic diagram is as follows.
This design has passed the vibration test specified in the standards of GB/T 2423.10 - 2008 / IEC 60068 - 2 - 6:1995, reaching the following levels: Frequency range: 10 Hz to 150 Hz
Test axes: X, Y, and Z axes
Displacement amplitude: 0.35 mm
Acceleration amplitude: 5 g
The performance data listed in this manual is obtained from tests in a standard laboratory environment and is applicable to general industrial equipment. The performance in actual applications may vary due to factors such as installation methods and combined stresses.
3. OK3562J-C Development Platform Description
3.1 OK3562J-C Development Board Interface Diagram
The connection of OK3562J-C SoM and the carrier board is board-to-board, and the main interfaces are as follows:
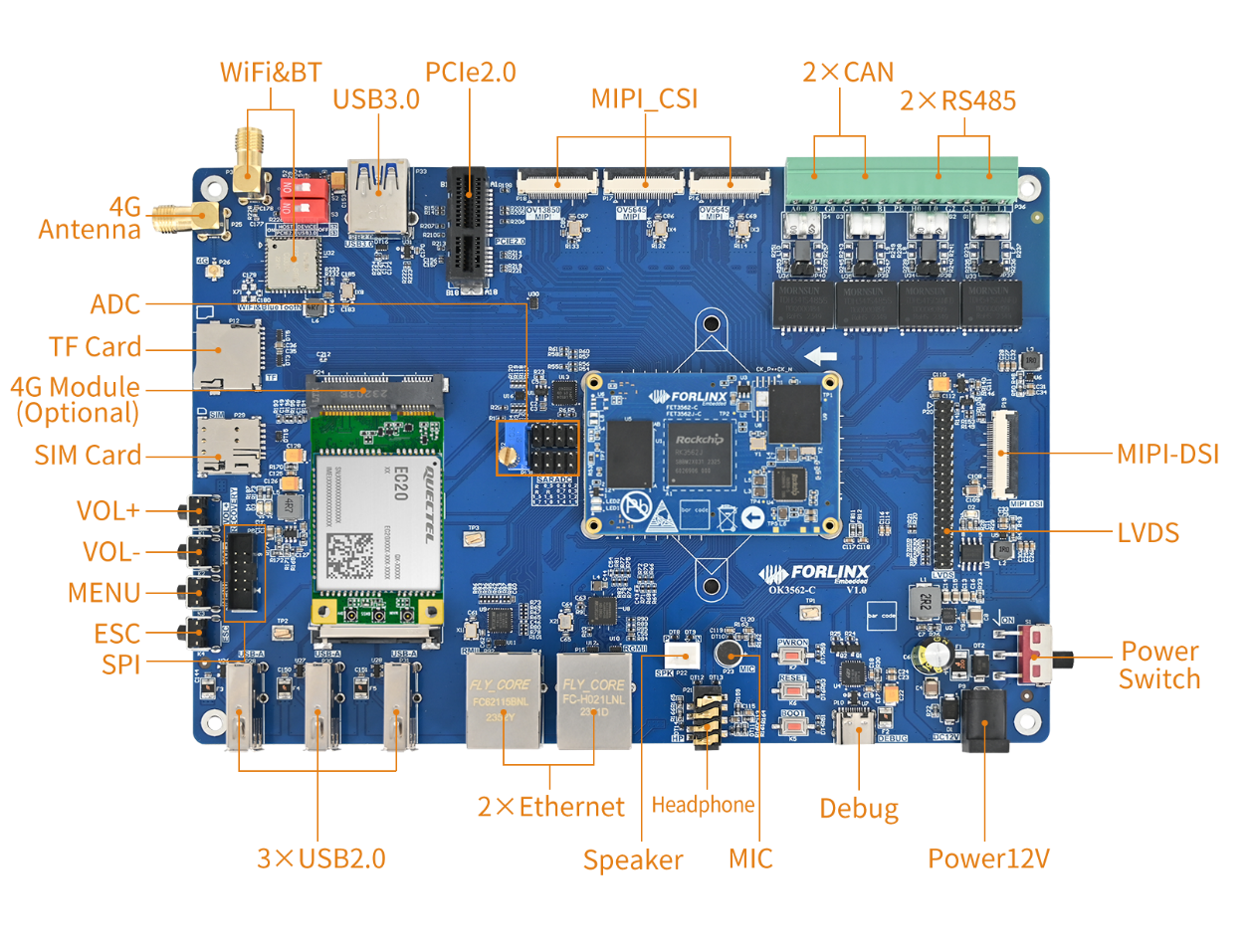

3.2 OK3562J-C SoM Dimension Diagram

PCB Size: 130mm × 190mm
Fixed hole size: spacing: 120mm × 180mm, hole diameter: 3.2mm.
Plate making process: thickness 1.6mm, 4-layer PCB.
Power supply voltage: DC 12V.
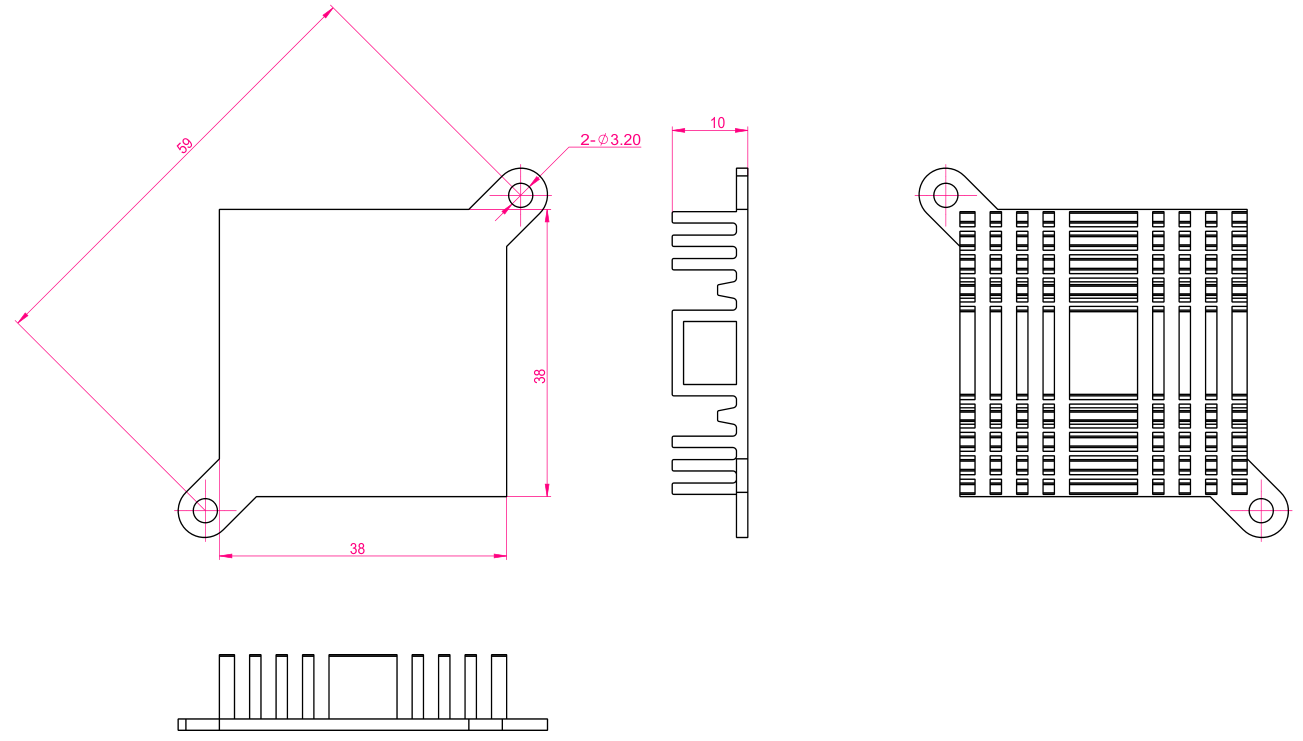
Two mounting holes with a diameter of 3.2mm are reserved on the carrier board. You can select and install the heat sink according to the site environment. Please add a layer of insulated heat-conducting silicone pad on the contact surface between the heat sink and the core board. 38Mm×38mm×10mm. For more detailed dimensions, please refer to the following figure.
3.3 Carrier Board Naming Rules
ABC-D+IK:M
Field |
Field Description |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
A |
Qualification level |
PC |
Prototype Sample |
Blank |
Mass Production |
||
B |
Product line identification |
OK |
Forlinx Embedded development board |
C |
CPU Type |
3562 |
RK3562 |
- |
Segment Identification |
- |
|
D |
Connection |
Cx |
Board-to-board Connector |
+ |
Segment Identification |
+ |
The configuration parameter section follows this identifier. |
I |
Operating temperature |
C |
0 to 70℃ commercial-grade |
I |
-40 to 85℃ industrial level |
||
K |
PCB Version |
11 |
V1.1 |
xx |
Vx.x |
||
:M |
Internal Identification of the Manufacturer |
:X |
This is the internal identification of the manufacturer and has no impact on the use. |
3.4 Carrier Board Resources
Function |
Quantity |
Parameter |
|---|---|---|
MIPI-DSI(1) |
1 |
4-lane MIPI-DSI, supporting capacitive touch screen and |
LVDS(1) |
1 |
4-lane LVDS, supporting capacitive touch screen and backlight |
CAN(3) |
2 |
Supports CAN2.0B, electrical isolation |
RS485(2) |
2 |
Electrical isolation |
MIPI-CSI |
3 |
Led out via FPC socket, 4lane+2lane+2lane |
WiFi |
1 |
Single antenna 2.4G & 5GHz Wi-Fi Dual-band 1X1 802.11ac +Bluetooth 4.2 |
Bluetooth |
1 |
|
USB3.0 |
1 |
The master-slave mode can be switched to use with PCIE. |
PCIe |
1 |
PCIe 2.1 can only be used in RC mode, only supports single |
4G |
1 |
4G module supporting miniPCIE interface, with USB2.0 |
TF Card |
1 |
Supports maximum SDR104 rate |
SPI |
1 |
Led out via box header connector |
KEY ADC |
4 |
Use 1 x SARADC to export 4 keys. |
USER GPIO |
1 |
User GPIO, key input + LED output |
USB2.0 |
3 |
USB HUB pinout, supports master mode only |
Ethernet |
2 |
1 x 100Mbps port and 1 x 1Gbps port are led out via RJ45. |
Audio |
Mono speaker connector, class-D, 1.3 W; |
|
ADC |
13 |
The pin header pin-out functions, which can be connected to |
RTC |
1 |
On-board CR2032 battery, keep going when power is off |
PWM |
1 |
Connect the display for backlight brightness adjustment |
UART Debug(2) |
2 |
Integrated in a Type-C port that can be connected to a |
JTAG Debug |
1 |
Note:
The parameters in the table are the theoretical values of hardware design or CPU;
There is interface multiplexing between MIPI-DSI and LVDS, and only one of them can be used;
UART9 is used for both debug and RS485. A DIP switch is used to select between the two functions;
Only the RK3562J has a CAN interface.
3.5 OK3562J-C Carrier Board Description
Note:
The component UID with “_DNP” mark in the diagram below represents it is not soldered by default;
The schematic diagrams in this manual are only for interface description. When users conduct hardware design, please refer to the source file materials.
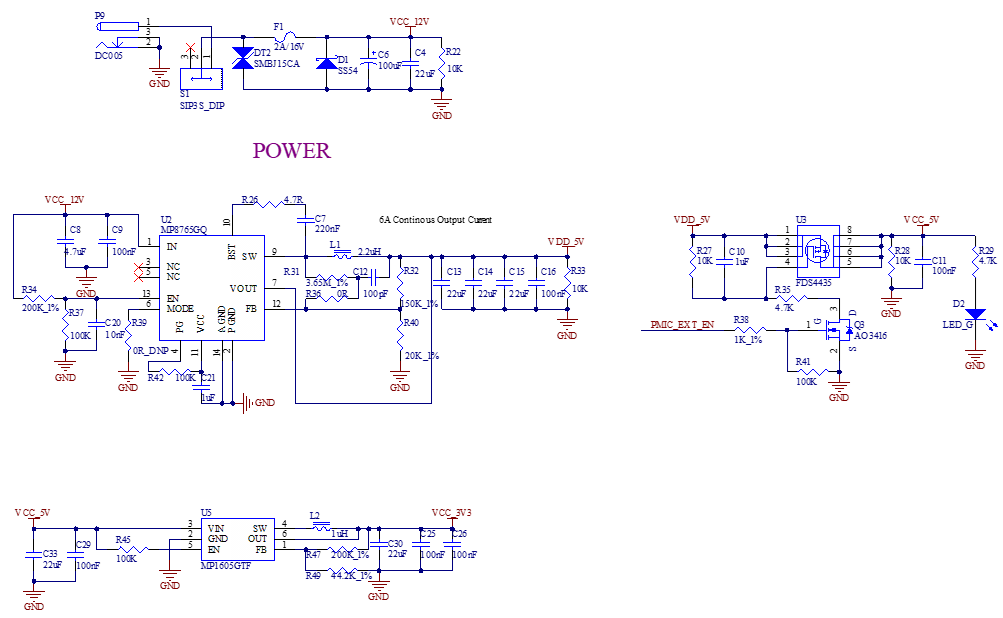
3.5.1 Carrier Board Power
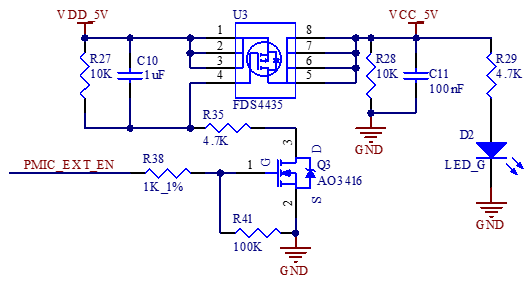
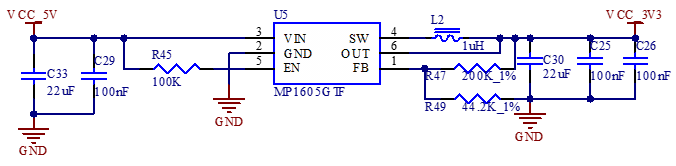
As shown in the figure, the 12 V DC power supply supplies power to the development board through the power socket P9. VDD_5V supplies power to the SoM. After the SoM is powered on, it outputs PMIC_EXT_EN to control the conduction of U3 on the carrier board. Then, VCC_5V supplies power to the carrier board devices.
PMIC_EXT_EN ensures that the SoM is powered on first and the carrier board is powered on later, preventing the latch - up effect from damaging the CPU.

3.5.2 Switch & Reset Key
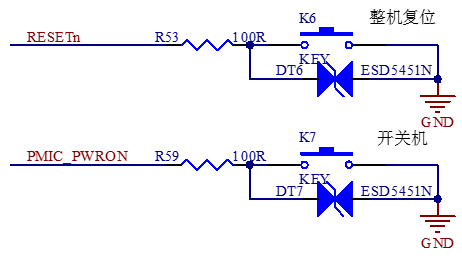
K6 on the carrier board is the development board reset key. Pressing it can realize the whole board power off and reset.
K7 on the carrier board is the development board power - on/off button. The board is set to start automatically when power is supplied by default. Long - press this button in the powered - on state to turn off the board, and then short - press it to turn it on.
3.5.3 SARADC Key
The carrier board uses one SARADC signal to realize the function display of the sampling key value through the key and resistance voltage division. The SARADC0_IN1_KEY/RECOVERY on the SoM is pulled up to 1.8V through a 10K resistor.

3.5.4 BOOT Configuration
The device OK3562-C determines the boot method by measuring the voltage at the SARADC0_BOOT pin. The SoM is already configured for this circuit, with the default boot priority as follows: FSPI, eMMC, TF Card, and then USB.
The FSPI is not welded on the SoM by default and only boots from the eMMC. System images can be flashed to the TF Card and USB.
If you use a USB cable to connect the board to a computer for image flashing, press and hold the K5 button while powering on the board to enter the Maskrom mode. Then, connect USB0 to the computer to flash the system.
If you use a TF Card to flash the image, you need to make a TF Card in advance. After inserting the card into the board and powering it on, the board will enter the TF - card flashing process. For the detailed flashing process, please refer to the software user manual.

Note: The SARADC0 _ BOOT signal is not available for other functions.
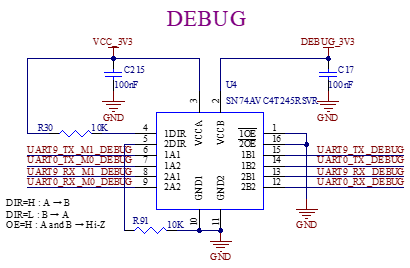
3.5.5 Debugging Serial Port
The carrier board integrates 2 x debug serial ports with one USB Type-C. Install the driver for CH342 on the computer, connect the P10 port to the computer, and debug serial port to start debugging.
UART9 is connected to both the debugging port and the RS485 port. You can use the DIP switch (reference designator S4) to select its function.


Note: To facilitate later debugging, please lead out these debug serial ports when designing the carrier board by yourselves.
3.5.6 JTAG/SWD
The development board supports two-wire JTAG/SWD interface, which is multiplexed with the TF card interface. Led out via a 2.54mm pitch pin.

3.5.7 RTC
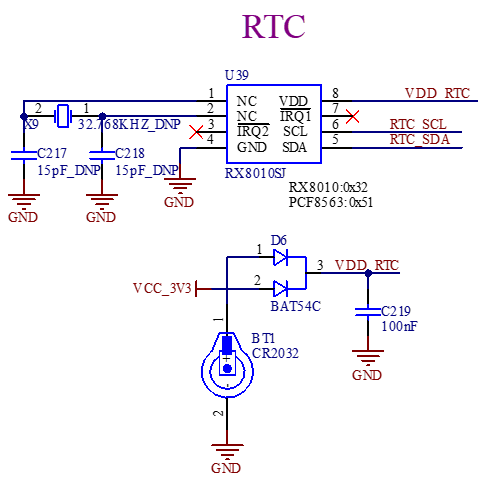
The carrier board is externally provided with RTC equipment through I2C1, and is supplied with power through D6 compatible with VCC _ 3V3 and the button cell. After the carrier board is powered off, the button cell can maintain power supply for the RTC chip. The RX8010SJ chip design is used by default. The button cell model is CR2032.
3.5.8 TF Card
The TF Card on the development board uses the SDMMC0 channel of the CPU. The power supply for the TF card uses the VCC_3V3_SD output from the SoM.


Note:
The pull-up resistor on the bus has been adapted on the SoM, so the pull-up can not be processed on the carrier board;
The TF card is a hot-swappable device, so ESD protection should be implemented;
SD signals must be length-matched.
3.5.9 SARADC
The SARADC is led out with 2.54mm - spaced pin headers. When paired with a sliding potentiometer, it can be directly connected via DuPont wires. The SoM has a total of 13 x SARADC, and the sampling voltage should not exceed 1.8V.

3.5.10 Ethernet
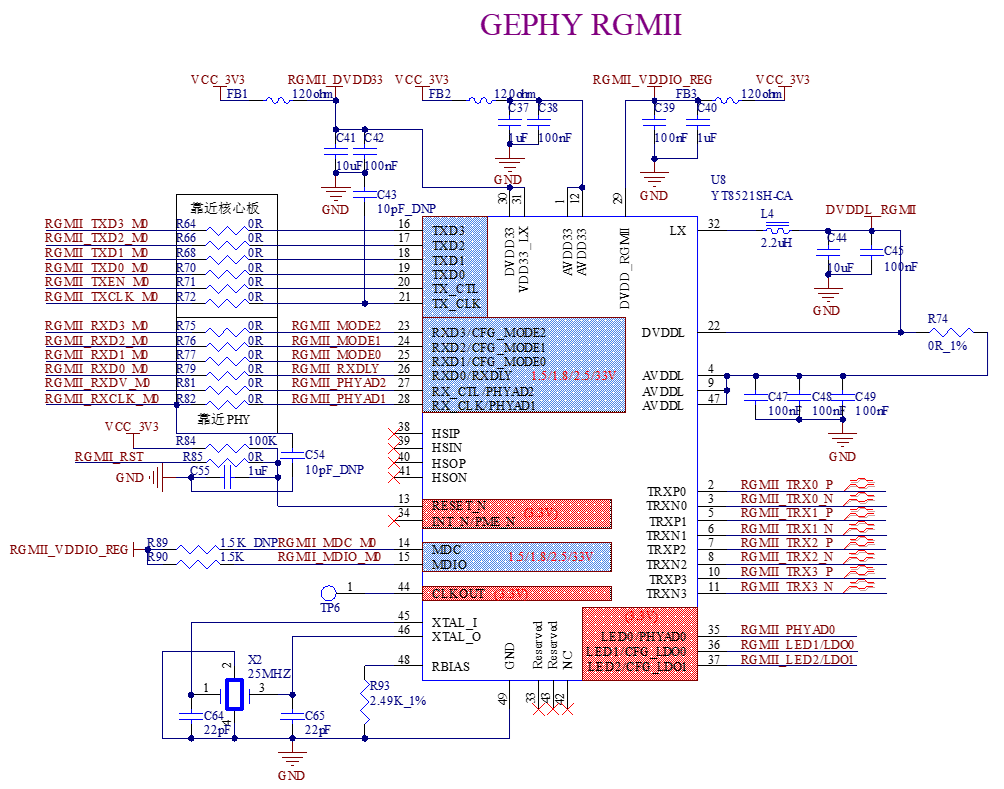
The development board supports 2 x native 1000M and 100M network ports. It uses the RGMII and RMII interfaces of the SoM, and is implemented in conjunction with the YT8521SH and YT8512H chips. These ports are led out through standard RJ45 sockets with network transformers, enabling external connection to network devices.

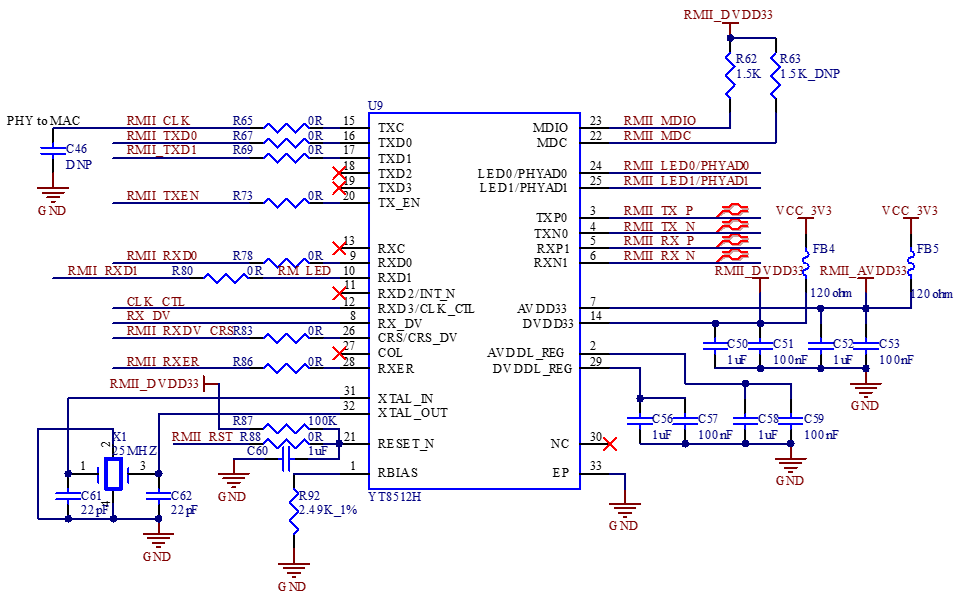

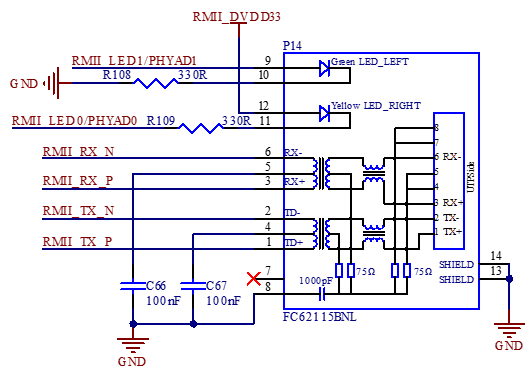
3.5.11 MIPI-CSI
There are three FPC sockets on the development board that can be connected to MIPI - CSI cameras. The connectors are 26P, with a 0.5mm pitch and a bottom - access flip - cover design.
The P17 and P18 ports support 2lane MIPI - CSI connections, while the P16 port supports 4 lane MIPI - CSI connections.


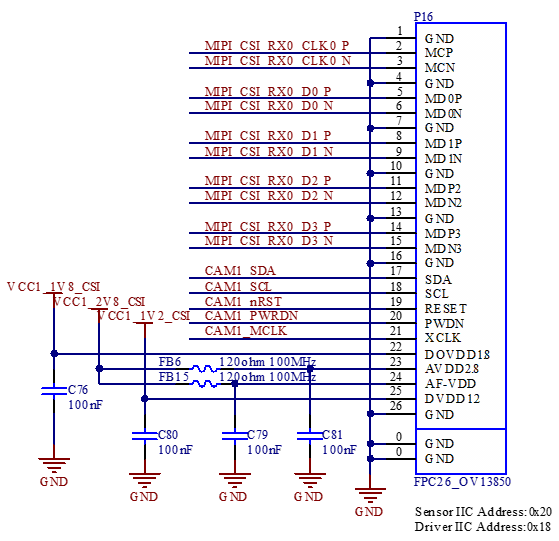
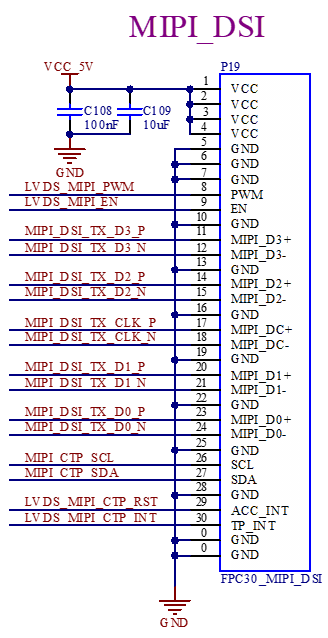
3.5.12 MIPI-DSI
The FPC socket with the reference designator P19 on the development board can be connected to a MIPI - DSI display. The connector is 30P, with a 0.5mm pitch and a bottom - access flip - cover design.
It supports 4 - lane MIPI - DSI connections and touchscreens with I2C interfaces. MIPI-DSI and LVDS screens can only be used alternatively, not simultaneously.
3.5.13 LVDS Display
The pin header P20 on the development board can be connected to an LVDS display screen. The connector has 38P with a 2.0mm pitch.
It supports 4 lane LVDS connectivity and I2C interface. MIPI-DSI and LVDS screens can only be used alternatively, not simultaneously.
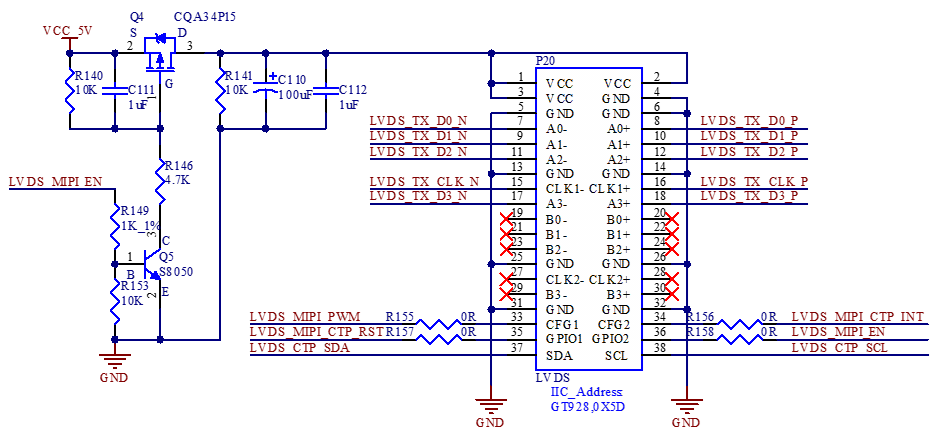
3.5.14 Audio
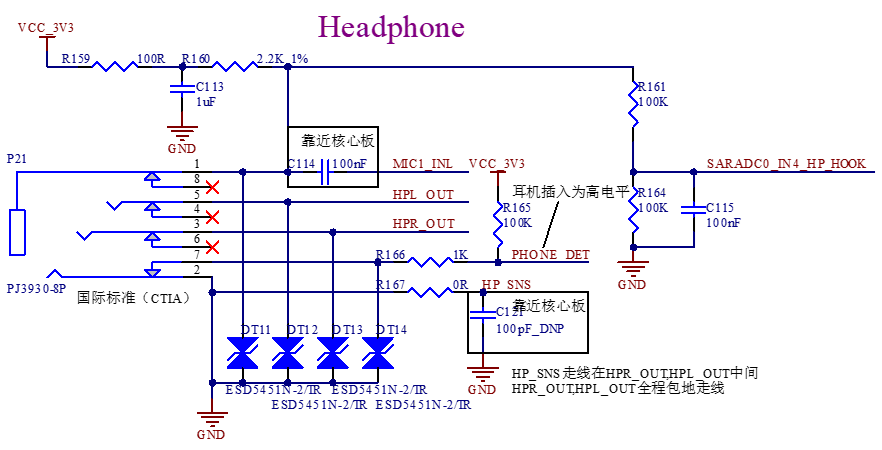
There is a standard 3.5mm headphone jack on the development board (CTIA international standard) at P21, supporting stereo headphone playback and mono MIC recording.
The P22 interface is a speaker interface, supporting mono Speaker, class-D, 1.3 W power.
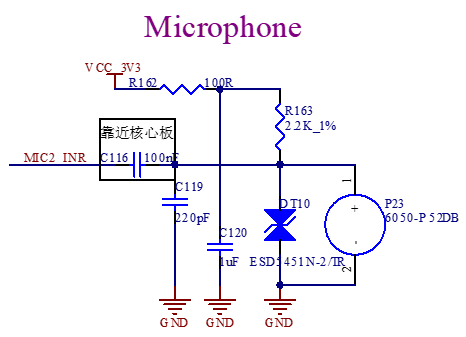
P23 is an onboard MIC that enables mono recording.

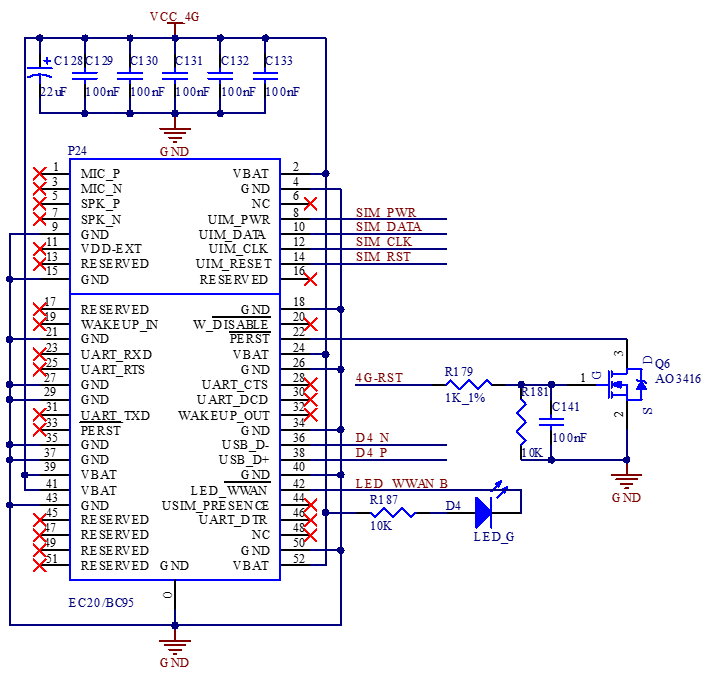
3.5.15 4G Module
The development board can be installed with a 4G module, and the supported specifications are miniPCIE interface, 3.3 V power supply, and USB2.0 communication.
P29 is a self - ejecting nanoSIM card slot. Please pay attention to the card insertion direction according to the markings on the board. Hot - swapping of the card is not supported.
Before using the 4G function, please power off the board first, install the 4G module and the SIM card, connect the 4G ipex jumper from the module to P26 on the board, and then an external antenna can be connected via the SMA interface of P25.


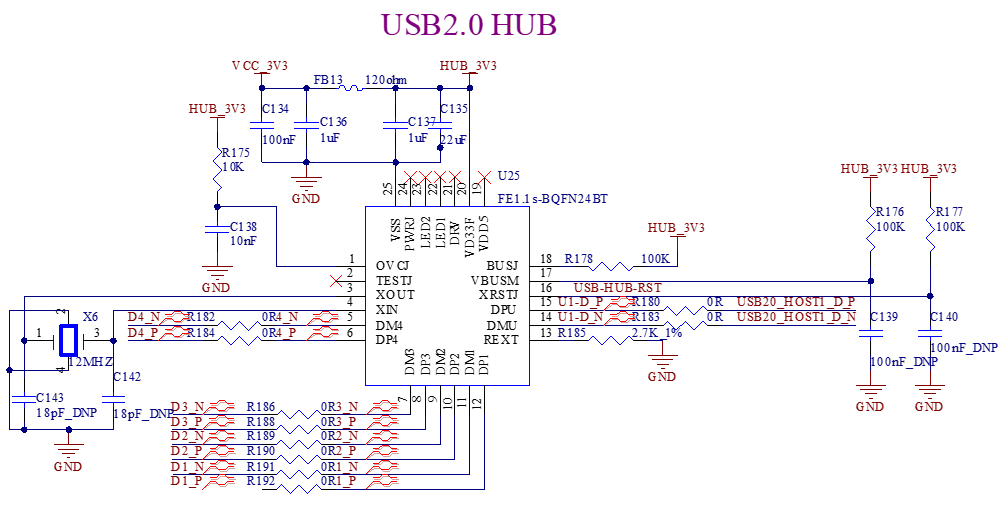
3.5.16 USB2.0
The development board is equipped with a built - in USB2.0 HUB, which expands four downstream USB HOST nodes. On the development board, these nodes are respectively connected to three standard USB2.0 - A interfaces and a mini - PCIE interface. The mini - PCIE interface can be connected to a 4G module.
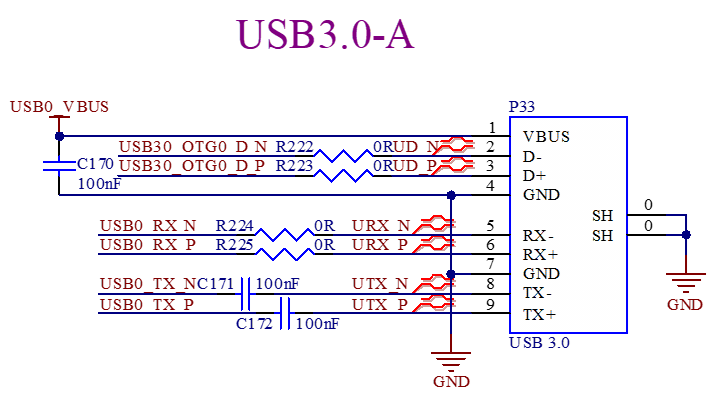
3.5.17 USB3.0 & PCIe
The SoM natively supports USB3.0 and PCIe2.1. However, these two functions share the same pins. The development board retains both functions and uses a high - speed analog switch chip and a one - bit DIP switch to control the selection. The USB3.0 is led out as a standard USB3.0 - A socket, and the PCIE2.1 is led out as a standard PCIE X1 socket.
PCIE can only do RC mode.
The USB3.0 supports master/slave mode, which is switched by a one-bit DIP switch.

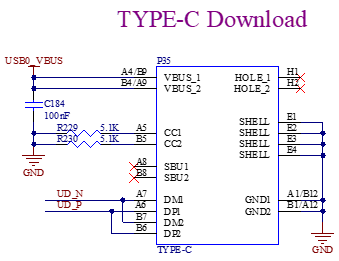
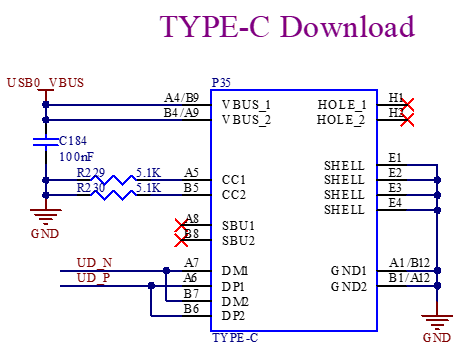
3.5.18 USB Download
The USB Type-C of P35 on the back of the development board uses the P/N differential signal in the USB3.0 (P33) signal and is designed as a Type-C interface for the convenience of users to connect to the computer for image programming and debugging.
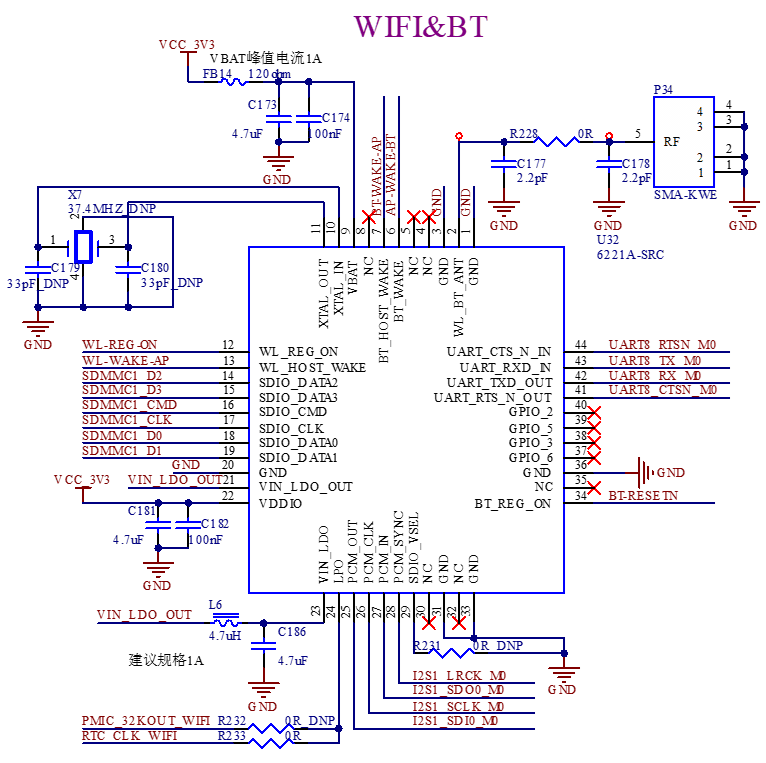
3.5.19 WiFi & Bluetooth
The development board is equipped with an integrated WiFi & Bluetooth module, with the module model Fn Link 6221A-SRC.
The WIFI uses SDIO interface, 2.4GHz and 5GHz dual-band, compliant with IEEE 802.11 a/B/G/n/AC, Bluetooth uses UART & PCM interface, compliant with BT 4.2 module.
P34 is SMA interface for antenna, please use 2.4GHz & 5GHz dual-band antenna.
3.5.20 CAN
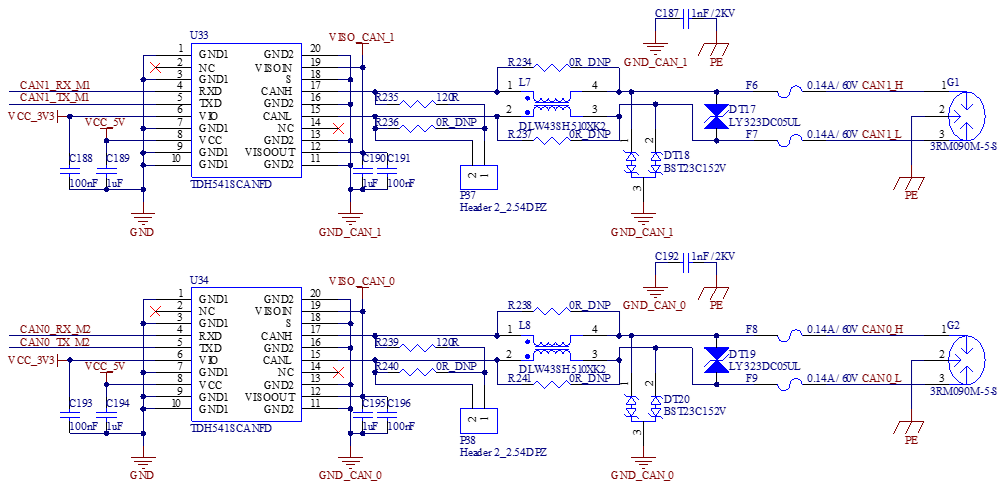
Two standard CAN interfaces are led out from the development board with CAN0 and CAN1. These interfaces support a maximum rate of 1 Mbps and are designed with electrical isolation, which can meet the protection requirements in most scenarios. Note that only the RK3562J has a CAN interface.
The CAN signal is led out through the green terminals at 3.81 mm pitch and a 120 ohm termination resistor is installed using a jumper cap.
3.5.21 RS485
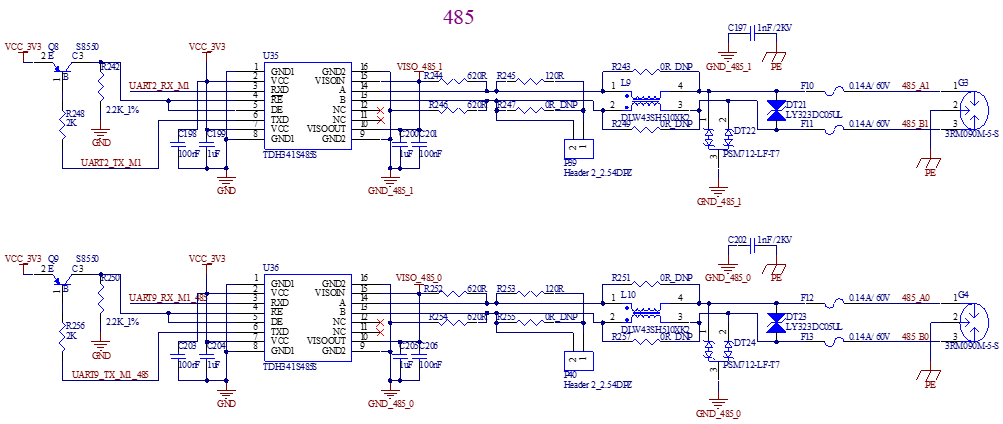
Two standard RS485 interfaces are led out by utilizing the native UART2 and UART9. These interfaces support automatic transceiver control and are designed with electrical isolation to meet the protection requirements in most scenarios.
The RS485 signal is led out through a green terminal with a 3.81mm pitch. Use a jumper cap to install a 120 - ohm terminal resistor.
UART9 is connected to both the debugging port and the RS485 port. You can use the DIP switch (reference designator S4) to select its function.
3.5.22 USER GPIO
Connect GPIO4_B7 to buttons and LED on the development board to demonstrate the functionality of GPIO.

3.5.23 SPI
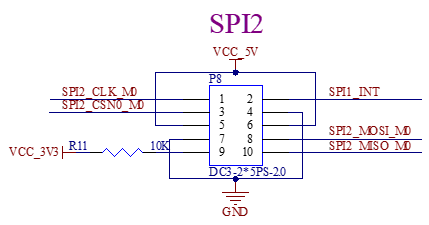
The SPI2 is led out separately from the development board, and the box header connector with a pitch of 2.0mm can be used for external equipment.
4. Connector Dimension Diagram
SoM connector: Board-to-board, 0.5mm pitch, 80P, male socket, height 1.23 mm, with locating post.

Carrier board connector: Board-to-board, 0.5mm pitch, 80P, female socket, height 1.85 mm, with locating post.

5. Development Board Linux System Whole - Machine Power Consumption Table
No. |
Test Item |
SoM Power |
Development board power (including SoM) |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
No-load starting peak power |
1.7W |
2.8W |
2 |
No-load standby peak power |
0.5W |
1.8W |
3 |
CPU + GPU + Memory + eMMC Stress Test |
2.2W |
3.2W |
4 |
7-inch LCD screen + 4G + U disk + video decoding |
1.8W |
7.3W |
5 |
SoM poweroff |
0.7mW |
- |
6 |
SoM sleep |
97mW |
- |
Note:
Test conditions: The SoM configuration is 2GB memory +16GB eMMC; the 4G module is Quectel EC20, and the screen is an optional product. SoM power supply is 5V and carrier board is 12V;
Power consumption is for reference only.
6. Minimum System Schematic
The minimum system includes the SoM, power supply, debugging serial port, and system image flashing interface.